Semaglutide is a medication that has gained attention for its effectiveness in managing type 2 diabetes and promoting weight loss. As with any medication, it is crucial to understand the potential side effects to make informed decisions about its use. In this article, we will provide a comprehensive analysis of the side effects associated with the use of semaglutide, based on available research and clinical trials.
Semaglutide is a medication that has gained attention for its effectiveness in managing type 2 diabetes and promoting weight loss. As with any medication, it is crucial to understand the potential side effects to make informed decisions about its use. In this article, we will provide a comprehensive analysis of the side effects associated with the use of semaglutide, based on available research and clinical trials.
Semaglutide is a glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1 RA) that mimics the action of a natural hormone in the body called glucagon-like peptide-1. It helps regulate blood sugar levels and appetite. Semaglutide is available as a subcutaneous injection and is used for the management of type 2 diabetes and obesity.
Common Side Effects
 Gastrointestinal Effects:
Gastrointestinal Effects:
The most frequently reported side effects of semaglutide are gastrointestinal in nature. These include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and constipation. In clinical trials, these side effects were usually mild to moderate in severity and tended to improve over time. Starting with a lower dose and gradually increasing it can help minimize these effects.
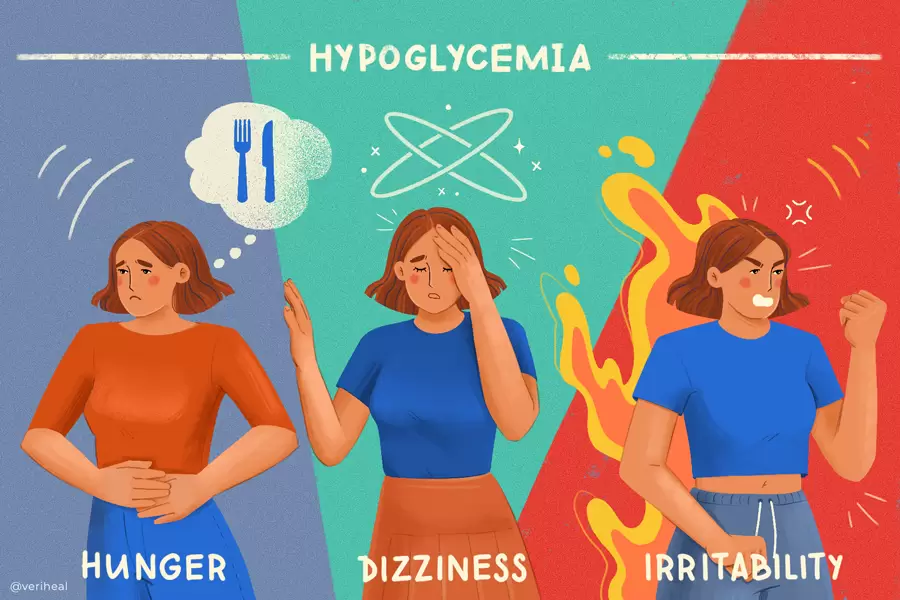
Hypoglycemia:
Semaglutide, like other medications used to treat diabetes, can lower blood sugar levels. Hypoglycemia, or low blood sugar, is a potential side effect of semaglutide. It is more likely to occur when semaglutide is used in combination with other diabetes medications that also lower blood sugar levels, such as insulin or sulfonylureas. It is important for individuals using semaglutide to be aware of the symptoms of hypoglycemia and take appropriate measures to manage it.
Less Common Side Effects:
Pancreatitis:
In rare cases, semaglutide has been associated with pancreatitis, which is inflammation of the pancreas. Symptoms may include severe abdominal pain that radiates to the back, nausea, and vomiting. Individuals should seek immediate medical attention if they experience these symptoms.
Thyroid Effects:
Semaglutide may affect thyroid function. Some individuals may experience an increase in thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) levels, which can indicate reduced thyroid function. Regular monitoring of thyroid function is recommended for individuals using semaglutide.
Gallbladder Effects:
Semaglutide can increase the risk of gallbladder-related adverse events, such as gallstones or inflammation of the gallbladder (cholecystitis). Symptoms may include abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting. Individuals with a history of gallbladder disease should discuss the potential risks and benefits of semaglutide with their healthcare provider.
Precautions and Considerations:
It is important to note that the side effects mentioned above are not exhaustive. Different individuals may experience varying side effects, and it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice. Healthcare providers should be informed about any pre-existing medical conditions, allergies, or medications to ensure the safe and appropriate use of semaglutide.
Semaglutide, like any medication, has potential side effects that individuals should be aware of. The most common side effects include gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and constipation. Hypoglycemia and rare but serious adverse events such as pancreatitis, thyroid effects, and gallbladder-related complications have also been reported. It is crucial to weigh the potential benefits against the risks and discuss any concerns with a healthcare professional. Regular monitoring and close communication with healthcare providers can help ensure the safe and effective use of semaglutide for the management of type 2 diabetes or obesity.